Back in #marchintosh earlier this year, there was a resurgence of setting up AppleTalk networks on a global scale. That was the start of GlobalTalk.
While the technology behind it existed all the way back in the 90s, AppleTalk networking at that time was being overtaken by the growing popularity of TCP/IP-based networking and AppleTalk was on the decline since then. There is just now a renewed interest on AppleTalk within the retrocomputing community.
While AppleTalk networks were primarily local area networks, Apple released a product that would interconnect remote AppleTalk networks by tunnelling through the TCP/IP-based Internet. This product was the Apple Internet Router; the “Internet” used here is the common noun form of an “interconnected network” and not the proper noun form referring to the global TCP/IP-based Internet.
I used to have AppleTalk networks, both LocalTalk and EtherTalk, at the home lab, but never really needed to connect them to the outside world. A weekend to spare provided the time for re-assembling the network and joining GlobalTalk.
First step is to set up a GlobalTalk router. There are now dedicated hardware devices that do this, using EtherTalk (AppleTalk over Ethernet), but I wanted to continue making use of the LocalTalk physical layer that is period-appropriate and used by other Apple machines at that time. I wanted to rebuild my Apple Quadra 605 anyway, for use in other projects, so this became my selected GlobalTalk router.
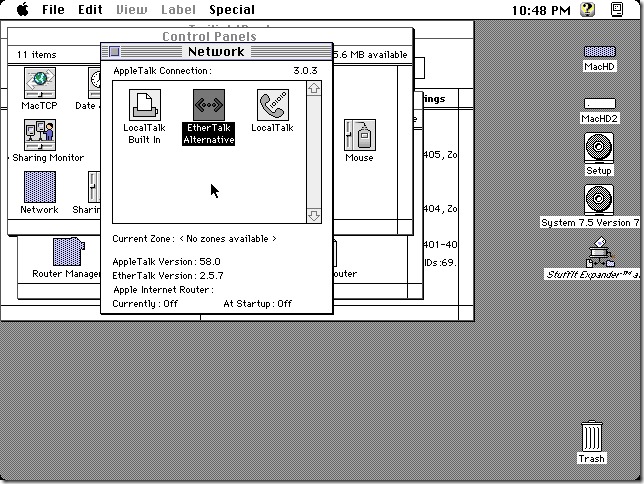
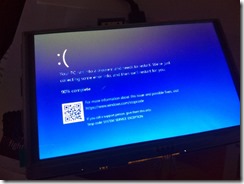
The Quadra 605 is a 68k-based Mac sharing the same specs with the LC475, Performa 475 and Performa 476. My preferred operating system is MacOS 7.6.1, the latest 7.x version, and what I have been using at the home lab more than ten years ago. Immediately hit a snag. Apple Internet Router (AIR) seems to require Classic Networking (MacTCP) instead of the later Open Transport framework. And on MacOS 7.6.1, whenever I try to switch Network selection from Open Transport to Classic Networking, it would state that Classic Networking is not supported with the machine CPU (Quadra 605 uses a 68LC040).
Back to square one and installing 7.5.5, the latest 7.5.x version, which would allow switching to Classic Networking. Fortunately, the advent of SCSI device emulators like BlueSCSI makes it so easy to rebuild older Macs. I installed an empty SCSI hard drive inside the Quadra 605, and used an external DB-25 BlueSCSI to bootstrap my installation. Aside from the ISO image for the System 7.5.3 installation CD, I only needed another custom Setup CD image containing the utilities that I often use, like ResEdit, DiskCopy, Aladdin Expander, System 7.5.5 upgrade disks, and the DaynaPort network drivers. For this setup, I also placed MacTCP Ping, Netscape Navigator 4.0.4 (works with Classic Networking), and the Apple Internet Router installation disks in the custom Setup CD and to the BlueSCSI microSD card.
What’s amazing about the BlueSCSI and similar devices is that aside from emulating SCSI hard drives and CDROM drives, the WiFi-enabled BlueSCSI (with the Raspberry Pi Pico W) also emulates a DaynaPort SCSI Ethernet device. That means I do not need to install an Ethernet card inside the Quadra 605. I used these SCSI Ethernet devices all the time with my older Macs and PowerBooks and am delighted to see them emulated in the BlueSCSI devices.
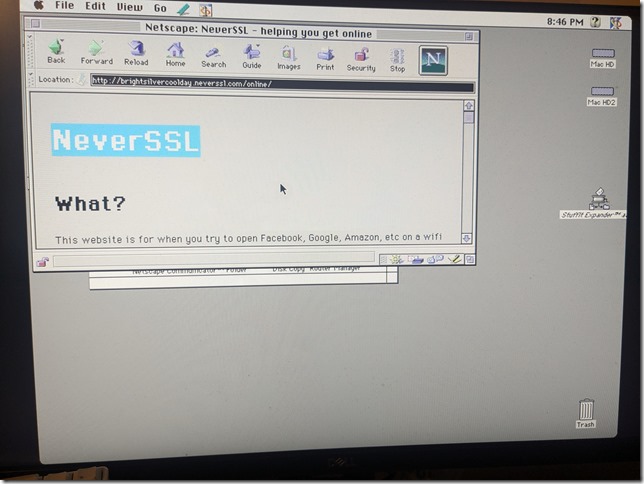
Once the DaynaPort drivers were installed, it was easy to set up MacTCP with a static local IP address, set the WiFi router as your gateway, and start wirelessly connecting to the rest of the Internet. I was readily browsing the web with Netscape Navigator. I typically try browsing http://neverssl.com to test connectivity. Do at your own risk.
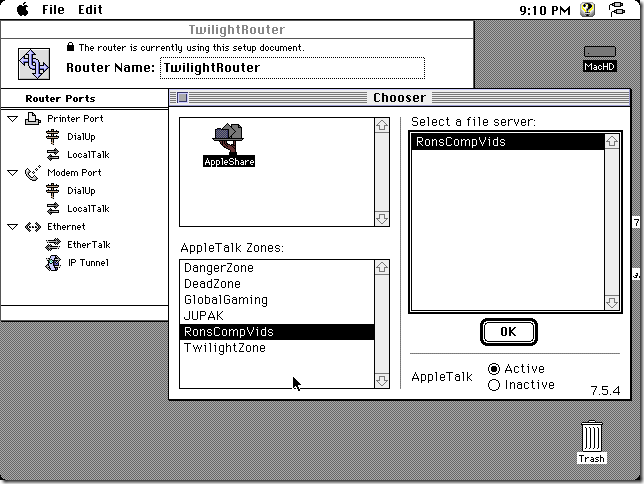
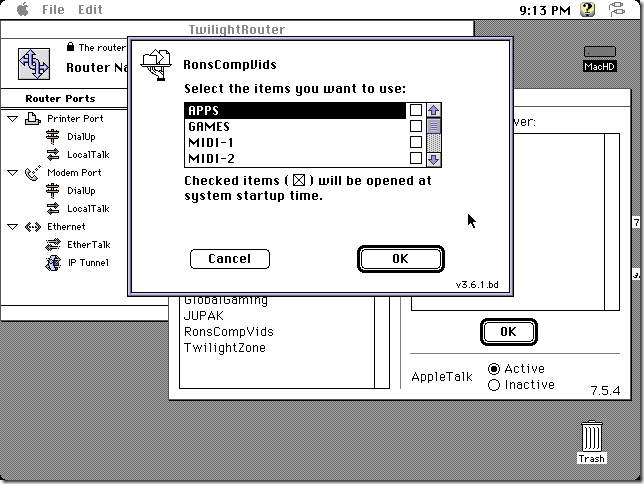
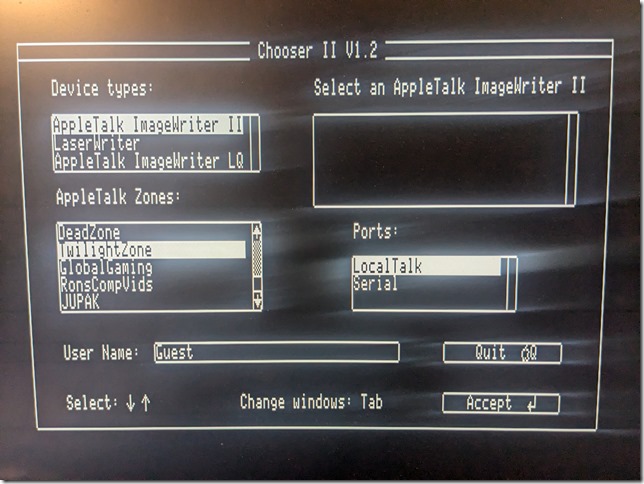
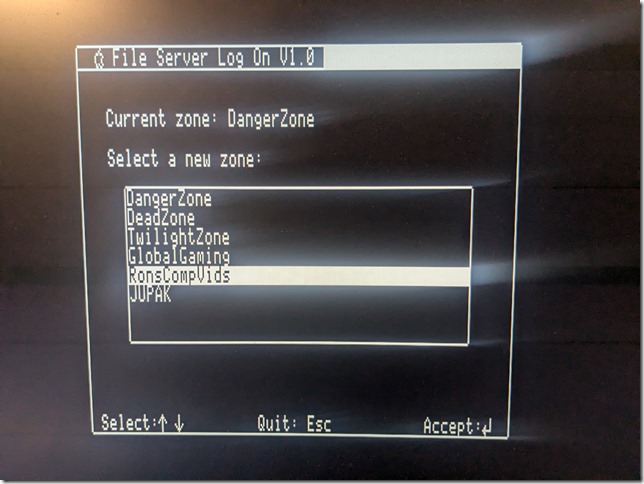
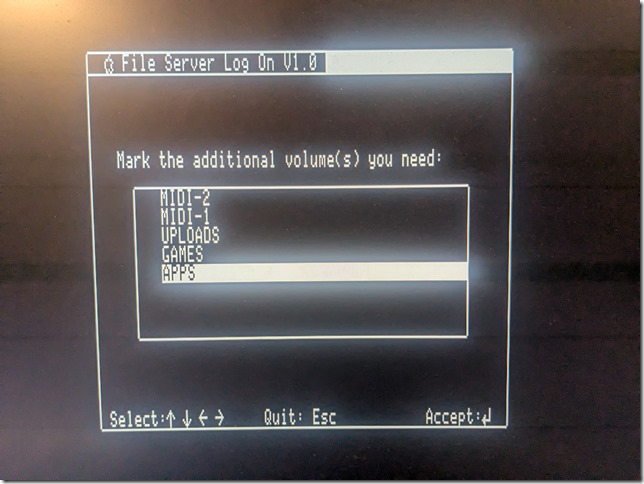
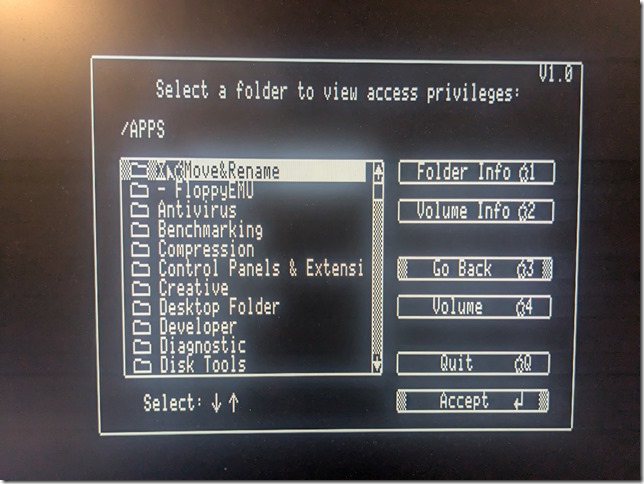
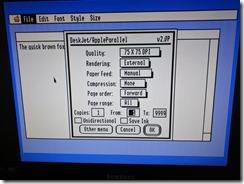
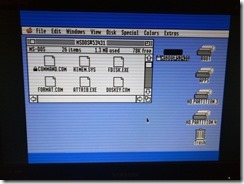
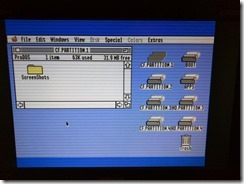
Another thing to set up is network sharing, in order to share local folders and printers. Sharing folders and printers are the most common use for AppleTalk and very popular in the GlobalTalk community. Shared folders are also visible and can be mounted in other AppleTalk-enabled machines within your local network, including an Apple IIe, an Apple IIgs, or even a DOS-based PC.
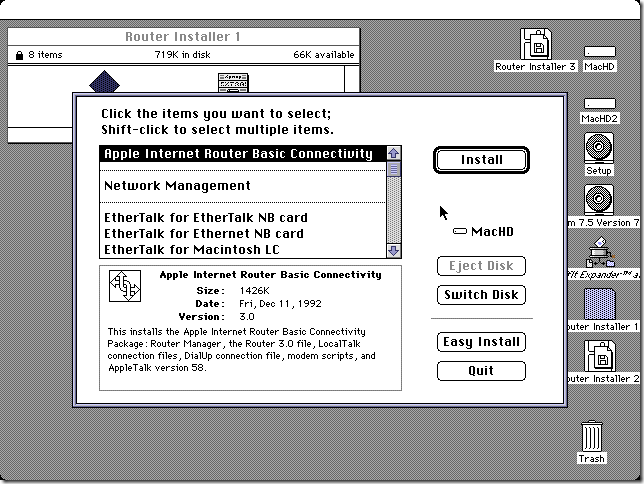
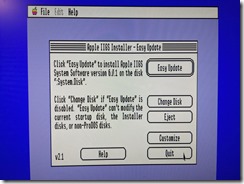
Once the local server has been set up, and Internet connectivity has been tested, the next step was to install Apple Internet Router. Sign up to join the GlobalTalk community and avail of the global network of AppleTalk routers tunneling AppleTalk through TCP/IP. The original AIR installation instructions for the GlobalTalk community is found here, and others have provided additional documentation. What follows are additional notes from my recent installation.
With System 7.5.5 installed and the Mac already connected to the Internet, the only other software needed to join GlobalTalk is the Apple Internet Router and the IP Tunnel Extension (AppleTalk/IP Wide Area Extension), both can be found here.
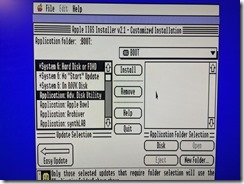
When installing Apple Internet Router, perform a custom installation and do not install the SNMP Network Management components. One of the SNMP Extensions causes a trap during system startup. If you happen to accidentally install the SNMP components, just remove or disable the SNMP AppleTalk Transport extension in the System Folder.
System 7.5.3 installation includes MacTCP 2.0.6, and there is a patch to bring it up to the latest version 2.1. Installing the AIR Router IP Extension (AppleTalk/IP Wide Area Extension to perform AppleTalk tunneling over TCP/IP) will downgrade MacTCP to 1.1.1 which is needed by AIR. Keep the MacTCP 1.1.1 version if you need to launch AIR and join the GlobalTalk network.
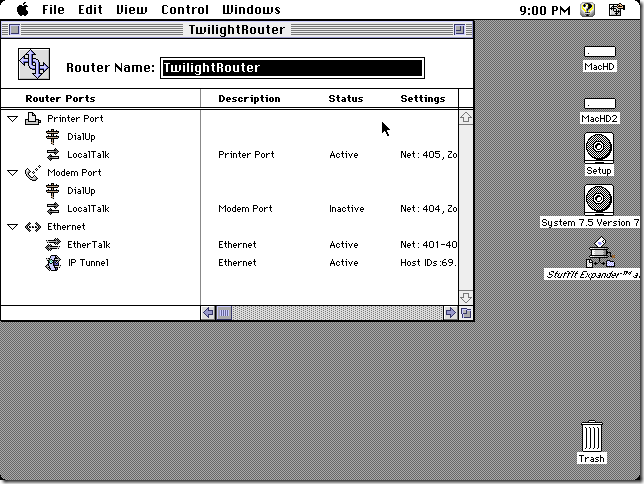
With the Apple Internet Router up and running, the local AppleTalk networks (either LocalTalk or EtherTalk) become visible to other AppleTalk networks that are connected using the IP tunnel. This is the GlobalTalk network.
Any other AppleTalk-aware machines, even an Apple IIe or Apple IIgs, in your local network will now be able to see the global AppleTalk networks with traffic being routed through the Mac running Apple Internet Router.
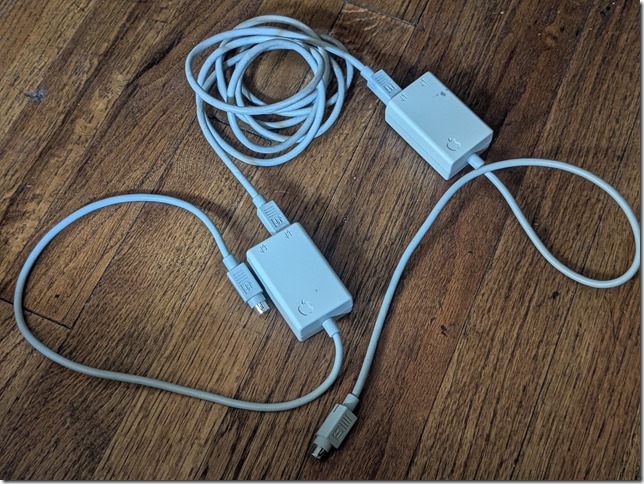
And for those who recognize the following, they are pre-Ethernet LocalTalk cables used in early Apple machines to establish a local area network that speaks AppleTalk. I’ve used an Apple IIe equipped with the Apple II Workstation Card to connect to my local LocalTalk network and, through the Apple Internet Router, browse shared folders and printers within the GlobalTalk nework.
Join up on GlobalTalk and enjoy retrocomputing and how file and printer sharing is done back in the early 90s.